AV:RetroTINK-4K
The RetroTINK-4K is an advanced video scaler from RetroTINK LLC. Building on the functionality of the RetroTINK-2X and RetroTINK-5X, the RetroTINK-4K offers high-end video scaling and processing at resolutions up to 4K60.
Overview
The RetroTINK-4K is the latest evolution of the RetroTINK line of video line doublers and upscalers. Below is a list of some standout features:
Output
- Digital Video up to 4K60
- Flexible output modes including 480p, 1080p, 1440p at various refresh rates
- Custom modelines on the SD card
- Fully buffered video (drop-free on input changes), Gen Locked and Frame Locked sync modes
- HDR10 output with full color correction to Rec. 2020
- High frame rate output modes: 1440p120, 1080p240
- Optional deep color output (10 bits at 4K60 may not be compatible with all displays)
- Up to 8-ch LPCM audio
Inputs
- Supports for virtually all analog formats:
- HD15/VGA: RGBHV, RGBS, RGsB, YPbPr, S-video and Composite
- SCART: RGBS, RGsB, YPbPr, S-video and Composite
- Rear RCA: RGsB, YPbPr and Composite
- Front Composite
- Front S-Video
- Digital Video Input supporting up to 1080p60/1200p (CVT-rb)
- Analog audio input sampled at up to 96kHz/24-bit with full gain control
- Optical TOSLINK audio input supporting 2-Ch LPCM or compressed surround
- Digital Video audio supports up to 8-ch LPCM
Analog Video
- Automatic gain calibration
- Automatic phase calibration
- Automatic input cropping to trim borders
- Full control of gain, offset and sample rate
- Console specific automatic sample rate detection (experimental feature)
- Support for a wide variety of off-spec arcade and PC boards (may require custom profiles to properly trim and center the image)
- Max input resolution of 1920x1080p60 or 1920x1200p60 CVT-rb
- Robust composite/S-video decoder with multi-region support (NTSC, PAL, PAL-60, SECAM)
Scaling
- Fully flexible, custom cropping and zooming in the horizontal and vertical space independent of other settings
- Automatic aspect ratio correction to 4:3 or 16:9
- Motion adaptive deinterlacing including film modes for 3:2 and 2:2 inverse telecine (experimental feature)
- RoTATE 90 deg CW or CCW (for 240p, 288p and 360p inputs)
CRT Simulation
- Multiple CRT beam profiles
- Fully configurable CRT beam strength and intensity modulation
- Adjustable CRT masks and strength
- Interlaced video simulation with offset scanlines
- LCD simulation patterns that automatically adapt to scaling, including non-integer factors
Image Processing
- End to end RGB pipeline with internal 12-bit precision
- Conventional gamma and approximated modes to minimize quantization error
- Advanced and fully configurable gamma and perceptual quantizer (HDR)
- Advanced color gamut transforms to simulate different display technologies
- Black frame insertion engine with customizable pattern and intensity
- Linear light processing
User Interface
- Advanced OSD menu based system
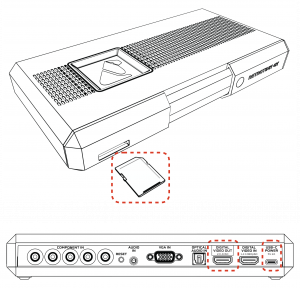
- SD Card for saving profiles, custom modelines and firmware updates
- Custom premium remote control
Getting Started
The RetroTINK-4K is designed to be powerful, yet easy to use and quick to setup. Here are some steps to get started Using the RetroTINK-4K:
- SD Card: A card is included with every RetroTINK-4K that includes the launch firmware and profiles. Please make sure this card is inserted in the device, as it is required for proper operation. If you lose the card, any FAT32 SD card 32 GB or less may be substituted.
- USB-C Power: Connect a USB-C cable supplying at least 5V/2A to the USB-C power input on the 4K.
- Video Output: Connect an HDMI™ cable (2.0 or higher / 18Gbps+) from the RetroTINK-4K output to your display.
- Video Input: Connect your device's signal to any of the RetroTINK-4K's inputs. More information on supported connections can be found in the Inputs section.
- Confirm Video Output: By default, the RetroTINK-4K outputs 4K60. If you don't see any picture, confirm that your display supports 4K60, or press the button on the remote that matches the resolution of your display (1080p, 1440p, or 480p). See the Remote and Output sections for more information.
- Select Your Input Source: Press the "Menu" button on the remote which will bring up the basic main menu. Go to the Input selections and choose the port and signal your device is using.
- Enjoy: Once your video source is visible, that is it! Enjoy the high quality, low latency scaling of the RetroTINK-4K. Time to play the game!
Basic Analog Calibration
With your game up and running, you may want to consider a couple more steps: (note that HDMI™ video sources do not require calibration)
| Auto Calibrate the Gain: Under Advanced Settings > RGB/Component ADC are the brightness controls for analog signals. Gain settings apply on a per-console basis.
| |
|
|
Crop The Picture: Under Advanced Settings > Scaling / Crop Setup will be the cropping controls. The RT4K positions the image based on how it's cropped, so this is how you get it to fill the screen the way you want it to. Crop settings apply on a per-game basis, and can be done manually or with Auto Crop.
|
Tweaks, Filters and Beyond
Of course, there is a lot more you can do with the RetroTINK-4K. Here are some more advanced options to explore:
- Update the Firmware
- Choose an Expert-Crafted Optimal Profile
- CRT and Scanline Effects
- Improve Image Vividness with HDR
- Improve Motion Clarity With Black Frame Insertion
Firmware Updates
The RetroTINK-4K can be updated to any firmware, with new firmware releases adding more new features as they are made.
- Power off your RetroTINK-4K and remove the SD card.
- Insert the SD card used for your RT4K into the SD card slot on your computer.
- Download the latest firmware .zip file from the RetroTINK website.
- Extract the contents of the .zip file to the SD card's root directory.
- Remove the SD card and insert it into the SD card slot on the RetroTINK-4K. Then, power the RT4K back on.
- On the RT4K remote, press the Menu button, then go to Advanced Settings > OSD/Firmware. In the Firmware update section, select "Check SD Card" to scan for the firmware file.
- If you have multiple firmware files on the SD card, the RT4K will always pick the most recent one.
- When a new firmware file is detected, a window will appear to confirm the install. Press right and then pick "[OK]" to begin installation.
- The RT4K will reboot for about 40 seconds, with the front LED flashing pink and then blue. Once done, it will power on again as normal. You're done!
All custom profiles, CSC files, banner images, input modes, mask overlays and modelines will be kept, as those are stored on the SD card instead of on the RT4K itself.
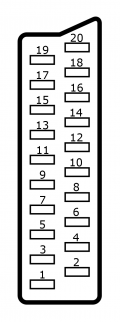
Inputs
The RetroTINK-4K features inputs for a wide variety of signals and connector types.
Front
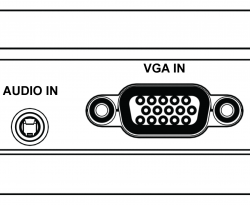
The RetroTINK-4K offers S-Video (over Mini-DIN) and Composite (over RCA) inputs in the front. The red and white RCA jacks are stereo audio inputs. Red/White front audio inputs are active when either the Front Composite or S-Video input is selected (assuming audio input override is not used).
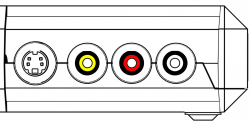
Rear RCA
The rear RCA jacks support YPbPr (component), RGsB, and CVBS (composite) inputs.
| Rear RCA Input | ||
|---|---|---|
| YPbPr | To use YPbPr (Component Video), connect the Red, Green and Blue YPbPr video cables to their corresponding colored RCA connectors, noting that the Red/White pair to the left is for stereo audio input. The maximum resolution supported is 1920x1080p 60fps, or 148.5Mhz | |
| RGsB | The Rear RCA input also supports RGsB, a flavor of RGB that sends the sync alongside the Green signal. To use RGsB (aka RGB Sync on Green), connect the Red, Green and Blue RGsB signals to their corresponding colored RCA connectors, noting that the Red/White pair to the left is for stereo audio input. The maximum resolution supported is 1920x1080p 60fps, or 148.5Mhz | |
| CVBS on Green | Composite video (CVBS) can be used with the Rear RCA input. To use CVBS, connect the composite signal connector to the Green RCA jack. The Red/White pair of jacks furthest left is for stereo audio input. The maximum supported resolution is 480i. | |
SCART
| SCART Input | ||
|---|---|---|
| RGBS (75 ohm) | RGBS is a form of RGB where sync is sent through a discrete line. The RetroTINK-4K accepts the following RGBS signal formats via SCART: Composite Sync (attenuated), Sync-on-Luma, and Sync-on-composite. They all work by sending information down the Red, Green, Blue, and "Sync" lines. The maximum resolution supported is 1920x1080p 60fps, or 148.5 MHz | |
| RGsB | RGsB sends sync down the green input, using only 3 cables. This RGB format is notably used by the PS2 when in 480p mode via SCART. The maximum resolution supported is 1920x1080p 60fps, or 148.5 MHz | |
| YPbPr | YPbPr is sent through the Green, Blue, and Red pins, respectively. The maximum resolution supported is 1920x1080p 60fps, or 148.5 MHz | |
| CVBS on Pin 20 | Composite video sent through Pin 20, usually through a composite to SCART adapter or if your cable uses sync-on-composite video and you wish to use composite instead of RGB. As with all composite signals, only 240p/480i/288p/576p signals are supported. | |
| CBVS on Green | Composite video can be sent through the Green pin. This would be useful if you use a component (YPbPr) to SCART adapter, just plug composite (yellow) into the Y RCA jack (Green). As with all composite signals, only 240p/480i/288p/576p signals are supported. | |
| Y/C on Pin 20/Red | S-Video (Y/C) can be send down Pin 20 (sync) and the Red pins. You will need a S-Video to SCART adapter. As with all S-video signals, only 240p/480i/288p/576p signals are supported. | |
| SCART Jack Pinout | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin # | RGBS (75 Ohm) |
RGsB | YPbPr | CVBS on Pin 20 | CBVS on Green | Y/C on Pin 20/Red | |
| 1 | Unused | ||||||
| 2 | Audio In - Right | ||||||
| 3 | Unused | ||||||
| 4 | Ground | ||||||
| 5 | Ground | ||||||
| 6 | Audio In - Left | ||||||
| 7 | Blue | Blue | Pb | ||||
| 8 | Unused | ||||||
| 9 | Ground | ||||||
| 10 | Unused | ||||||
| 11 | Green | Green+Sync | Y | CVBS | |||
| 12 | Unused | ||||||
| 13 | Ground | ||||||
| 14 | Unused | ||||||
| 15 | Red | Red | Pr | Chroma (C) | |||
| 16 | Unused | ||||||
| 17 | Ground | ||||||
| 18 | Ground | ||||||
| 19 | Unused | ||||||
| 20 | Sync | CVBS | Luma (Y) | ||||
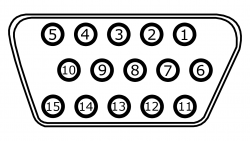
HD-15
| HD-15 Input | ||
|---|---|---|
| RGBHV | RGBHV is a form of RGB where information is sent through 5 lines: Red, Green, Blue, Horizontal Sync, and Vertical Sync. The maximum resolution supported is 1920x1080p 60fps, or 148.5 MHz. This is most common for PC sources. | |
| RGBS | RGsB sends sync down the green input, using only 3 cables. This RGB format is notably used by the PS2 when in 480p mode via SCART. The maximum resolution supported is 1920x1080p 60fps, or 148.5 MHz | |
| RGsB | RGsB sends sync down the green input, using only 3 cables. This RGB format is notably used by the PS2 when in 480p mode via SCART. The maximum resolution supported is 1920x1080p 60fps, or 148.5 MHz | |
| YPbPr | YPbPr is sent through the Green, Blue, and Red pins, respectively. The maximum resolution supported is 1920x1080p 60fps, or 148.5 MHz | |
| CBVS on Hsync | Composite video sent through the horizontal sync line. As with all composite signals, only 240p/480i/288p/576p signals are supported. | |
| CBVS on Green | Composite video can be sent through the Green line. As with all composite signals, only 240p/480i/288p/576p signals are supported. | |
| Y/C on Green/Red | S-Video (Y/C) can be send down Green (Y) and the Red (C) pins. As with all S-video signals, only 240p/480i/288p/576p signals are supported. | |
| HD-15 Jack Pinout | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin # | RGBHV | RGBS | RGsB | YPbPr | CBVS on Hsync | CBVS on Green | Y/C on Green/Red | Data | |
| 1 | Red | Red | Red | Pr | Chroma(C) | ||||
| 2 | Green | Green | Green+Sync | Y | CVBS | Luma(Y) | |||
| 3 | Blue | Blue | Blue | Pb | |||||
| 4 | Unused | ||||||||
| 5 | Ground | ||||||||
| 6 | Ground | ||||||||
| 7 | Ground | ||||||||
| 8 | Ground | ||||||||
| 9 | Unused | ||||||||
| 10 | Ground | ||||||||
| 11 | Unused | ||||||||
| 12 | External Transmit (EXT TX) | ||||||||
| 13 | Horizontal Sync | Sync | CVBS | ||||||
| 14 | Vertical Sync | ||||||||
| 15 | External Receive (EXT RX) | ||||||||
Digital Video
| The RetroTINK-4K supports many resolutions digitally up to 1920x1080p60 or 1920x1200p60 CVT-rb. Unlike standard consumer equipment, the RetroTINK-4K can tolerate and adapt to arbitrary and off-spec resolutions. |
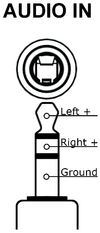
3.5mm TRS Audio
| The RetroTINK 4k-Pro allows for audio through a 3.5mm TRS input. This accepts stereo analog audio. By default, this is associated with the HD-15 port. |
Optical Audio
| The RetroTINK 4K-Pro offers a discrete optical audio TOSLINK input. This input 2-channel LPCM and compressed surround sound. |
Alternate Audio Inputs
The RetroTINK-4K allows you to reassign audio inputs from their default video source. Go to Advanced Settings, select "Audio Input" under "Acquisition". The "Input Override" option under "Source" allows the audio for the current input video input to be taken from a different audio source. The only exception is that it is not possible to assign HDMI (TM) audio to a non-HDMI (TM) video source. The reverse, however, is possible.
| Picture | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RCA (Rear) | The leftmost two RCA inputs in the rear. White and Red, | |
| HD15 | The 3.5mm TRS input in the rear. | |
| SCART | The SCART input on the side. Audio is fed in through pins 2 and 6. | |
| Front | The red and white RCA inputs in the front of the unit. | |
| SPDIF | Optical audio fed through a Toslink input. |
HDMI™ Output
The RetroTINK 4K-Pro only outputs via the Digital Video output port. Note that The RetroTINK 4K-Pro can not output through any of its analog ports.
The HDMI™ Output menu allows you to set your output resolution, enable black frame insertion, change your colorspace output (colorimetry) and more. Here is a breakdown of some key functions:
Output Resolutions
The following outputs are readily supported by the RetroTINK 4K-Pro. Also noted are resolutions available by pushing their respective button on the remote. If you are unsure which resolution to use, use the buttons on the remote.
| Resolution | Description | Remote Button? |
|---|---|---|
| 4k60 | Default resolution and framerate for 4k displays, aka 3840x2160p.
Default Resolution for the TINK 4K-PRO |
Yes |
| 4k50 | Intended for PAL games and 24Hz content. | No |
| 1080p60 | Default resolution for 1080p displays. | Yes |
| 1080p50 | Intended for PAL games. and 24Hz content | No |
| 1440p60 | Default resolution and framerate for 1440p monitors, aka 2560x1440p. | Yes |
| 1440p50 | Intended for PAL games and 24Hz content | No |
| 1080p100 | Intended for PAL games and 24Hz content with BFI | No |
| 1440p100 | Intended for PAL games and 24Hz content with BFI | No |
| 1080p120 | Intended for NTSC content with BFI | No |
| 1440p120 | Intended for NTSC content with BFI | No |
| 480p60 | Minimum suggested output resolution for modern displays, aka 720x480p.
Pressing the Reset button on the back of the unit activates this resolution. |
Yes |
| 2880x2160p70.00 | Intended for off spec content from retro computers | No |
| 1920x2160p60.00 | No | |
| 800x600p60.00 | Output for retro computers. | No |
| 1920x1200p60 | 5x output for consoles intended for 8:5 (16:10) displays. | No |
Sync Lock
Older video game consoles didn't always have perfect video timings. CRTs typically had no problems working with these variances, but these "imprecise" consoles can sometimes have trouble working with modern TVs and capture devices that conform to a more rigid standard. Some games, such as Silent Hill or Chrono Cross on the PlayStation 1, will alternate between 240p or 480i video modes if you are in-game or in the items/pause menu, respectively. On many displays, upscalers and capture devices, this will create a long delay and a "no input detected" screen for several seconds while the device reorients to the new video mode. The issue of a device taking a gameplay-harming amount of time to change between video modes has been colloquially called the "Chrono Cross" problem.
Sync Lock controls how the RetroTINK-4K synchronizes the output frame rate with the input frame rate and handles these input changes. Triple Buffer operates the output independently from the input which results in a stable output signal even if the input signal glitches or changes. However, this comes at the cost of a variable lag, usually between a fraction of a frame to a fraction of a frame plus one whole frame. On occasion, you will see judder when frames needed to be dropped or repeated.
Gen Lock is the recommended mode as long as your display is compatible with the source's refresh rate. Gen Lock loosely couples the output frame rate with the input frame rate. After a few seconds, the output frame rate will lock with the input frame rate and achieve minimum lag without screen judder.
Frame Lock tightly couples the input and output frame rates. Any change in the input frame rate will cause a disruption in the output signal and a hard resynchronization.
Variable Refresh Rate (VRR)
The RetroTINK-4K can flag the output as VRR. While the RetroTINK-4K itself never outputs variable frame rates, settings this flag may be useful to force the display to accept a broader range of refresh rates. It is also useful on some displays to prevent re-buffering and other frame rate changes which will interfere with the RetroTINK-4K's BFI generator.
Colorimetry
HDMI Output Colorimetry specifies the colorspace of the HDMI output. By default, the Auto setting will select Rec. 709, and toggle to Rec. 2100 when HDR is enabled. You may wish to manually set output to Rec. 2020 (without HDR enabled), Adobe RGB or DCI-P3 if your display supports a wider color gamut. This may improve the image quality/accuracy when using the settings in the Color Correction menu.
HDR
HDR, located under Advanced Settings > Digital Output, is a way for the RetroTINK-4K to output a much more luminous picture for TVs that support it. HDR is intended for use with either Black Frame Insertion or Scanlines and Masks, as it helps compensate for the darkened image.
- Currently, the only option available is "HDR10 [8-bit]".
The table below shows two photos of an LG-CX displaying the RT4K using the "PVM 600 TVL" profile, under the HDR CRT Simulation folder. It's impossible to communicate the luminance of HDR in SDR, so here the camera had its exposure set for the HDR photo first, demonstrating the luminance gain compared to the SDR photo.
| HDR Comparisons - Off-screen Photos | |
|---|---|
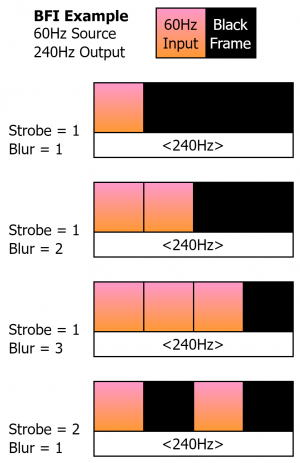
Black Frame Insertion (BFI)
Black Frame Insertion (BFI) is a technique to improve motion clarity with high refresh rate monitors. As an example, a 60fps video source played on a 120hz monitor could have a black frame interstitially placed between every frame. The resulting "image-black-image-black" pattern can increase the perception of motion and fine details. If you have a higher refresh rate monitor, a customizable example can be viewed over at Blur Busters.
To enable BFI:
- Set a Supported Resolution: The RetroTINK-4K can generate BFI, but due to bandwidth constraints, BFI is limited to 1440p or lower resolution output. When the Output Resolution is not set to a high frame rate output (100 or 120hz) BFI Controls will be disabled.
- Set a supported Sync Lock Mode: BFI also cannot be enabled unless you are in Gen or Frame Sync Lock mode.
| Black Frame Insertion (BFI) Settings | ||
|---|---|---|
| Strobe: Strobe controls how the output frame rate is divided into the input frame rate. As depicted in the diagram, with Strobe 1, the 60Hz input frame is flashed one time at 240 Hz. At Strobe 2, the 60Hz input frame is flashed twice at 240Hz, with black frames in between. Alternatively, a 60Hz source within a 120Hz output would display for 1/2 of the time 120Hz output window.
Blur: Blur is a duty cycle modifier that works in relation to Strobe to change how many frames the source video is presented in relation to the black frames. In the example diagram (60Hz Source inside a 240Hz output), a Blur of 1 would display the source video 1/4 of the 120Hz window, a Blur of 2 would display the source video 2/4 of the 120Hz window, and a Blur of 3 would display the source video 3/4 of the 120Hz window. Some relationships of Blur and Stobe are locked, such as a 60Hz video source in a 120Hz output window, which would only allow a Blur of 1 (1/2 of the output 120Hz window). | ||
More information about BFI can be found at Blur Busters.
Remote
| RetroTINK-4K Remote Diagram | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Button | Description | Button | Description | Button | Description | |
| Power | Powers on / off the Tink 4K | 11 | Profile 11 | 4K | Switches to 3840x2160p 60Hz | |
| INPUT | Input Source Selection Menu | 12 | Profile 12 | 1080p | Switches to 1920x1080p 60Hz | |
| OUT | Digital Video Output menu | MENU | RetroTINK-4K Main Menu | 1440p | Switches to 2560x1440p 60Hz | |
| SCL | Scaling/Crop Setup | BACK | Back button | 480p | Switches to 720x480p 60Hz | |
| SFX | Image Processing | △ | Up | RES1 | Custom Output Resolution 1 | |
| ADC | Enters Acquisition menu matching the current input | ◁ | Left | RES2 | Custom Output Resolution 2 | |
| PROF | Profiles | ENTER | Enter | RES3 | Custom Output Resolution 3 | |
| 1 | Profile 1 | ▷ | Right | RES4 | Custom Output Resolution 4 | |
| 2 | Profile 2 | ▽ | Down | AUX1 | ||
| 3 | Profile 3 | DIAG | Diagnostic Console | AUX2 | ||
| 4 | Profile 4 | STAT | Status | AUX3 | ||
| 5 | Profile 5 | AUTO-GAIN | Auto Calibrate Gain | AUX4 | ||
| 6 | Profile 6 | AUTO-PHASE | Auto Calibrate Phase | AUX5 | ||
| 7 | Profile 7 | PLAY/PAUSE | Pause current screen | AUX6 | ||
| 8 | Profile 8 | SAFE | AUX7 | |||
| 9 | Profile 9 | SYNC-GEN | Sync Lock Gen | AUX8 | ||
| 10 | Profile 10 | SYNC-BUF | Sync Lock Triple Buffer | - | ||
Scaling/Crop
Input Crop
The RetroTINK-4K has robust controls to adjust size, positioning and cropping. For most users, the CP Auto Crop function will trim the unused blank space around the image, and stretch the remaining image to fit the boundaries of the screen. Note that only RGB and Component sources function with Auto CP. Top, Bottom, Left and Right Crop variables can also be manually set.
Vertical Pre-Scale
The RetroTINK-4K features the ability to "Pre-Scale" video content, or discard scanlines, at a fractional increment of the source input. Discarding vertical lines results in a loss of vertical resolution. This loss can be useful under certain circumstances, such as creating more accurate scanline rendering for 240p visual content output from consoles that run at higher resolutions (such as the Dreamcast or Wii).
RoTATE
RoTATE (pronounced "Roh-tah-tay") is a special feature within the RetroTINK-4K to rotate the image 90 degrees clockwise or counterclockwise. This is especially useful for games that may only display their image horizontally, such as many arcade shooters.
To enable RoTATE, the samples per line of your video source must be lower than 1024 samples per line. Because the video S-video and Composite is locked to 858 samples per line, no additional tweaking is required when using these input sources. For RGB or YPbPr input, Please see "RGB/Component ADC" (link) section for information on ADC and decimation settings to meet this requirement. Similar limits apply when using HDMI™ sources. Supported resolutions include 240p, 288p or 360p. Please use the "HDMI™ Receiver" menu if the horizontal samples exceed 1024 (for example MiSTer cores that use pixel repetition).
CP Auto Crop
The RetroTINK 4K-Pro can automatically crop and set aspect ratio for an input if it is fed a sufficient game screen. Letterboxed, pillar-boxed, and window-boxed screens are not recommended. Please see what the options do below:
| Name | Effect |
|---|---|
| Vertical Only | Automatically adjusts "Top Trim" and "Bottom Trim" to the top and bottom of the game image. Does not adjust Left Trim or Right Trim, and does not change Aspect Correction |
| Full Crop to 4:3 | Automatically adjusts Left, Right, Top, and Bottom Trim to the image, and changes Aspect Correction to 4:3 (PAR) |
| Full Crop to 16:9 | Automatically adjusts Left, Right, Top, and Bottom Trim to the image, and changes Aspect Correction to 16:9 (PAR) |
Profiles
Profile Management
Included Profiles
Community Profiles
Profile Troubleshooting
Advanced Settings
Automatic Settings
Automatic Sampling Detection
The RetroTINK 4k can take advantage of sampling and scaling algorithms to seamlessly change settings when it detects a horizontal resolution change. This is useful for most analog retro gaming consoles, but requires knowledge of their "Master Sampling Rate," noted below.
| Console Name | Master Sampling Rate | Available Resolutions |
|---|---|---|
| Super NES | 3410 | 256x224, 256x239, 512x224 |
| Sega Genesis/Mega Drive | 256x224, 320x224 | |
| Sega Saturn | ||
| Turbo Grafx 16/PCEngine | 2730 | 256x224, 320x224 |
| Sony Playstation | 256x224, 320x224, 384x224, 512x224, 640x224 | |
| Sony Playstation 2 |
Once you know the master Sampling rate of your console, set that console's ADC Sample rate in the "Sample Rate Detection" menu under ADC Sample Rate, and turn both "Auto Dec. Factor" and "Auto Dec. Phase" to "On." Once you enable those options, if you know which resolutions you'll use, scroll down to that resolution to enable that horizontal resolution's detection and the RetroTINK 4K-Pro should automatically switch to a different set of settings whenever it detects that particular resolution is used. This process will help automatically set Decimation Factor and Decimation Phase in the ADC setup.
Automatic Color Calibration
For RGB and YPbPr sources ONLY. If you are able to find a sufficiently large patch of color that should be white in your game screen, make your way to the RGB/Component Setup page (click the ADC button on the remote) and make your way down to the "Auto Calibrate" option. Selecting this makes the RetroTINK 4K-Pro automatically calibrate your color based on that white patch. You may need to manually adjust the individual colors a few ticks more to get the true RGB code 255,255,255 for a color.
Automatic Phase
Any game screen is sufficient for automatic phasing, but it is recommended to use the 240p Test Suite or other sufficiently patterned screen for eyeballing results. whether you've set automatic sample detection using that menu, or you manually selected Decimation Factor in the ADC page, selecting Auto-Calibrate Phase makes the RetroTINK 4K-Pro automatically select the best Decimation Phase and Sub-Phase for your current picture and should give you the sharpest results. It is recommended you run this 3-5 times to make sure the same factors and phases are consistently chosen.
Image Scaling
Console Specific Methodology
Nintendo NES / Famicom
The Famicom (or Family Computer) is the original Japanese version of Nintendo's landmark console, while the NES (or Nintendo Entertainment System) was released in all other regions. All Famicom / NES systems will be marked as such on the front, so simply read that to tell which one yours is (particularly useful regarding the top-loading redesigns). These systems render games in 256x224.
- The NES family renders and outputs all audio in mono via the white RCA jack (left speakers). To account for this, go to Advanced Settings > Audio Setup, then set Input Swap to "Mono (Left)".
The NES / Famicom can only output either Composite video or RF (with one rare exception). You will need at least a composite signal to connect directly to the RT4K. Use the list below to tell which one your system outputs:
- Composite signals are supported by the RetroTINK-4K. This can be used on either the front yellow plug, or the rear green plug.
- Original "Front-loading" NES (NES-001).
- Top-loading "AV Famicom" with the rounded power switch and flat cartridge slot.
- Sharp's "Twin Famicom".
- Sharp's "Famicom Titler" (also capable of S-Video).
- RF signals are not normally supported by the RetroTINK-4K. These models support RF output:
- Original Famicom w. hard-wired controllers.
- Revised "Top-loading" NES with a rounded cartridge slot and power switch.
- The RF Modulator output from the original "Front-loading" NES-001, which has softer sound compared to the the sharper Composite output.
Super NES / Super Famicom
The majority of Super NES / Famicom games run in 256x224 resolution, while a select few games run with a mix of the following: 512x224 in the whole screen for menus, 256x224 for most of the image while running 512x224 over certain parts of the screen to create transparency effects, or the same but using 512x224 resolution to allow sharper text on the screen. It is recommended to run the Super NES in 512x224p mode to make sure you get all available detail. (https://consolemods.org/wiki/AV:RetroTINK-5X_Pro#512_%22Hi_Res%22_Games)
We recommend using a Super NES model number SNS-001, or Super Famicom model number SHVC-001, and an RGB SCART cable wired for Sync-on-Luma, as this works with both of the aforementioned models. There are internal revisions of these models, noted as "1-Chip" on the motherboard, and the 1-Chip-03 does not work with Composite Sync. There is a revised model, SNS-101 and SHVC-101, also known as the Super Nintendo Junior. This model only supports composite video.
[Picture Here: 1-Chip without gain adjustments vs 1-Chip with gain adjustments]
As noted, there are revisions of the original model Super NES, noted by the "1-chip" on the motherboard. The 1-chip boards have sharper yet brighter video, while the non-1-chip boards have a "smeared" and slightly darker look. We encourage using the auto-gain functions in the ADC to correct the video on both models.
[Picture Here: Non-1-Chip vs 1-Chip]
Profile included for automatic switching between 512 and 256 in Display Aspect Ratio, for both SCART and HDRV YPbPr cables.
Super GameBoy
The Super GameBoy Cartridge allows you to play original style GameBoy and GameBoy Color cartridges on your TV using the Super Nintendo, and adds borders. Once dialed in, GameBoy games are rendered in a 160x144p window inside a 256x239p canvas. However, GameBoy games were expected to be displayed on the square pixels of their screens, unlike the rectangular CRT pixels that the SNES expects.
- For correct Super GameBoy pixels, go to "Advanced Settings > Scaling/Cropping, then set Aspect Correction to "1:1 (Sq. Pixel)".
[Picture Here: Generic SGB vs Optimized 15x]
Profile included to maximize the GameBoy window to the screen.
Nintendo 64
All stock N64 support Composite, all NTSC N64 support S-Video, some PAL N64 do not support S-Video, and French N64 support SECAM S-Video.
All N64 have 3 levels of video processing that keeps it from being sharp:
- All games scale their image to 640 pixels wide. Many games were rendered at different resolutions but the N64 will scale to 640.
- Many games render at 320 pixels wide and, as a trick, you can double your ADC Decimation factor to "correctly" render games in their original resolution. This trick only works for games that render at 320 pixels wide, and do not work for games that render at other resolutions that are not 320 or 640 pixels wide.
- Software level anti-aliasing. This can be disabled by patching ROMs or using a Gameshark to disable the effect.
- Hardware level anti-aliasing. This can't be disabled without a physical mod.
[Picture Here: AA enabled vs AA disabled]
[Picture Here: a 320 game with the trick used vs left at 640 (should be the same)]
[Picture Here: a non-640 or 320 game with the trick used (should look worse)]
Pokemon Stadium GameBoy Tower
Pokemon Stadium's GameBoy Tower allows you to play Pokemon games on your TV, similar to a Super GameBoy, and even uses the Super GameBoy borders. The issue, however, is the scaling noted above. These games render at 160x144p inside a 256x239p canvas, which is then scaled to 640 pixels wide. You will not get a sharp picture out of this setup due to that factor alone. It is recommended to play in a generic or default profile.
[Picture Here: SGB vs Pokemon Stadium]
Nintendo GameCube
For the purposes of use with the RetroTINK 4K-Pro, it is highly recommended to use a DOL-001 GameCube, which has the digital out port, and an Insurrection Industries Carby which outputs crisp digital video and can connect to the Digital Video input port of the RT4K. If you insist on buying YPbPr cables, we can only recommend the OEM D-Terminal cable with a D-Terminal to Component adapter, or the OEM component cable.
Most GameCube Games will run at 480p, a progressive mode is activated by holding B when the GameCube boots up a game.
Swiss, the Anti-Flicker Filter, and Horizontal Frame buffer Width
While Most GameCube games run at 480p and progressive mode is relatively easy to access, many GameCube games use an "anti-flicker-filter" by default, which will soften the image. Most of these filters can't be turned off in-game, but the homebrew software Swiss will allow you to boot games, including your own disks, with the anti-flicker filter turned off. As an added bonus, newer versions of Swiss automatically turn the filter off and boot your game in 480p.
[Picture Here: game with anti-flicker filter on vs off]
[Video here: Smash Bros Melee turning the flicker filter on and off]
A few GameCube games scale their image to fit the console's frame buffer before output. Swiss allows you to turn this off and shows the image at its original framebuffer width, and you can use the RT4K to scale it back, for a small sharpness gain.
[picture here: Framebuffer width left alone and the framebuffer width option turned on, with the RT4K used to scale back to the intended resolution] (I don't know what game to use)
240p Games
There are 2 GameCube games that run at 240p: Megaman X Collection, and the NES games in the Zelda Collector's Edition Promotional Disc. This means you do not have to enable 480p to run those games and can sharply scale these games on the RT4K.
[Picture Here: Megaman X on Super NES vs GameCube]
GameBoy Player + GameBoy Interface
The GameBoy Player is a popular add-on to the GameCube that allows you to play GameBoy, GameBoy Color, and GameBoy Advance games on your TV. The GameBoy Player Disk does not sharply render games onto the screen, but you can use the homebrew software GameBoy Interface to sharply render games into the RT4K. A specific flavor of GBI was created to take advantage of the Insurrection Industries Carby and the TINK 4K's Digital Video input. Please use files gbihf-rt4k-HDMI.cli, gbihf-rt4k-HDMI.dol+cli or gbihf-rt4k-HDMI.gci included with GBI and follow the instructions noted here.
[Picture Here: GBA game on RT5x scaled to 4k (12x scale) vs RT4K (13x scale)]
[Picture Here: GBC game on RT5x scaled to 4k (12x scale) vs RT4K (15x scale)]
Profiles included for 13x scaled GBA games and 15x scaled GBC games.
Nintendo Wii
The Nintendo Wii is a very versatile console: it plays GameCube Games, Wii Games, and many classic retro titles through emulators as part of the Virtual Console lineup. The Wii also has easy to find YPbPr component cables and can easily support 480p across all Wii software through its component cables, making it a popular option for playing GameCube games. The Wii only supports 3 resolutions: 720x240p, 720x480i, and 720x480p. Please read on for more information on getting the sharpest possible picture from a Wii.
Profile included for basic generic output. It is recommended you use this for basic Wii use.
Virtual Console
Many Virtual Console games output at 240p when the Wii is in SDTV mode, and they will line double to output at 480p in EDTV mode. All virtual console games scale the image to 640 pixels wide, so it is recommended you use the default or generic profiles for playing virtual console games. Also of note: NES Virtual console games are rendered many shades darker than an orignal console, as an anti-epilepsy measure.
[Picture Here: Donkey Kong on Super NES vs Donkey Kong on Wii with generic settings]
USBLoader GX, and Counteracting the Anti-Flicker Filter, 480p LPF, and the Framebuffer Video Width
Homebrew called USBLoader GX allows you to activate or deactivate code before running games, even on your disks.
Most Wii games will apply an anti-flicker filter, even at 480p, which results in a softer picture. Use USBLoader GX's options to turn this off for Wii Games. If you wish to run GameCube games, you will need to turn the anti-flicker filter off separately in either Nintendont or Devolution, but USB-Loader GX does have these options in its menu.
[Video here: Super Smash Bros Brawl's settings menu turning the anti-flicker filter on and off]
There is an option in USBLoader GX called the "480p pixel fix" which makes the game look much sharper. It only works with RVL-001 models with the internal CPU-01 motherboard.
[Picture here: Wii game with 480p pixel fix off vs on]
You can get even sharper picture from the Wii by enabling the "Video Width: Framebuffer" option in USBLoader GX. This will make games output in their original rendering resolution, which you can then rescale using the RT4K to get a much sharper picture than originally intended at the "correct" aspect ratio. As an added bonus, NES and Super NES games will render at 512x224p with this option turned on, which you can use a doubled decimation factor to treat a game like its original 256x224 resolution, and get picture on par with their original consoles.
[Picture Here: Megaman X Super NES Optimal vs Wii Optimal]
Nintendo WiiU
It is highly recommended to use the WiiU's HDMI output instead of its Component output. This is because the analog video is duller, and has less sharpness (even compared to Component from the PS3 and 360).
- The WiiU's HDMI only outputs in limited range. To account for this, go to Advanced Settings > HDMI Receiver, then set Input Range to "RGB Lim.".
Nintendo Switch
NSO Games
it is highly recommended to use 1080p output for the NSO emulators and turning on "Pixel Perfect" in their settings under "Game Screen" and to also turn off "Show controls in game" under "Control Display," and to turn off "reproduce classic feel" on the GameBoy and GameBoy Advance apps. This way, all games output a perfectly integer scaled, line-multiplied output for their games.
[Picture here: Donkey Kong Country Super NES Optimal vs Switch Optimal vs Switch no adjustments] For a 256 wide game
[Picture here: Ristar Genesis on Wii Optimal vs Switch Optimal vs Switch no adjustments] for 320 wide games
[picture here: Mario & Luigi Superstar Saga on GBI 13x vs Switch Optimal 13x vs Switch no Adjustments 12x] for GBA games
[Picture Here: The Legend of Zelda, Oracle of Ages on GBI 15x vs Switch Optimal 15x vs Switch no adjustments 14x] for GBC games
Sega Master System
Recommended output: RGB
Sega Genesis/Mega Drive
Recommended output: RGB
For practicality, "Genesis" refers to both the Sega Genesis and the Mega Drive (it's Japanese and European name), as they are functionally identical as far as the RetroTINK-4K is concerned, outside of NTSC and PAL standards.
- The Sega Genesis has three "240p" output resolutions: 320x224, 256x224. A third resolution, 480i, is only known to be used in the 2 Player VS modes of Sonic the Hedgehog 2 and Combat Cars.
Certain Genesis games will display coloured dots along the bottom edge of the screen. Known as CRAM (Colour RAM) dots, these would have been in the overscan area of most CRTs and thus invisible to the player, but are quite prominent on modern displays. You can hide them by going to Advanced Settings > Scaling/Cropping and adjusting the Bottom Trim value. You should not use Auto Crop, as it will consider the CRAM dots to be the bottom edge of the picture.
Composite effects. see this portion of the 5x wiki https://consolemods.org/wiki/AV:RetroTINK-5X_Pro#Genesis_Dithering
Sega CD
Sega 32x
Master System Games on Genesis
Sega Saturn
Recommended output: RGB
Sega Dreamcast
Recommended Output: RGBHV
Sony PlayStation
All Sony Playstation models support RGBS. It is recommended to use a well shielded SCART cable that uses Sync-on-Luma.
Resolution Switching
PlayStation games will switch resolutions often, usually horizontal resolutions like 256, 320, 384 and 512, but occasionally vertical resolutions as well with 480i. The PlayStation is a perfect use for the Automatic Sampling Detection feature of the RT4K. To help with switching vertical resolutions quickly, please enable Triple Buffer in the RT4K's Output menu.
see this part of the 5x wiki https://consolemods.org/wiki/AV:RetroTINK-5X_Pro#Resolution_Switching
Profiles included will automatically switch to all resolutions. You may want to consider researching your game collection and see if you can turn off any resolutions that you won't use, for faster response from the auto sampling detection.
Sony PlayStation 2
The PS2 outputs 240p, 480i, 480p, and 1080i, and supports RGB as well as YPbPr. For simplicity, it is highly recommended to use YPbPr cables because the RT4K will automatically detect and switch to all those resolutions seamlessly. The PS2 will use RGBS for 240p and 480i, but will switch to RGsB for any resolutions above that. While the RT4K supports RGsB, it does not automatically switch from RGBS to RGsB, you will need to change the input manually.
All PS2 games will output either 512 pixels wide or 640 pixels wide. [sic]
PS1 Backwards Compatibility
PS1 games on PS2 use a different set of optimal sampling numbers than the PS1 console.
Sony PlayStation Portable
PSP models PSP-2000, PSP-3000, and PSP-N1000 (aka PSP GO) can output to a display. It is highly recommended you use component cables with the RT4K.
PSP games are rendered at 480x272p. When they are displayed on a television with component cables, they render a 480x272p picture inside of a 720x480p canvas. You can use the RT4K to upscale the image to fit the screen. You will get the sharpest integer scaled picture at the expense of cutting off 2 vertical pixels.
[Picture here: PSP left alone (4.5x scale) vs PSP scaled to 8x]
PSone Classics on PSP
PSone Classics are PS1 games played on the PSP, and use a different set of optimal sampling numbers than the PS1 and PS2 consoles.
- PSone Classics can be output at their original resolution. On the PSP, go to Settings > Connected Display Settings, then set Component / D-Terminal Output to "Interlace".
[picture here: ps1 console optimized vs ps1 classic]
Sony PlayStation 3
The PS3 supports HDMI, which is recommended for the sharpest possible picture with the RT4K.
- The PS3 supports outputting PS3 games at 720p, 1080i and 1080p, which the RT4K supports. However if you do not have an option enabled (such as 720p), the PS3 will use a different one. To avoid this, on the PS3 go to Settings > Display Settings, then pick "Video Output Settings". In the new menu, choose "HDMI", then "Custom". In the list, ensure that 720p, 1080i and 1080p are all selected, then press Right and then X to save your settings.
- While the PS3 does support up to 1080p using component cables, it's softer compared to HDMI output. However many users choose it anyway, as the PS3's HDMI output always uses HDCP (High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection) with no option to disable it like on PS4 and PS5.
[Picture Here: HDMI vs YPbPr]
PSone Classics on PS3
PSone Classics on PS3 can render to 480p, but scale the image to fit the 4:3 aspect ratio. For the sharpest picture, use these settings:
- On the PS3, go to Settings > Game Settings, then set both PS - Upscaler and PS - Smoothing to "Off".
- On the RT4K, go to Advanced Settings > Scaling/Cropping, then set Vert. Pre-Scale to "1/2".
[Picture Here: PS1 console optimized vs ps1 classic]
Sony Playstation TV
The PSTV allows you to play Vita, PSP, and PS1 Classics on your TV through HDMI. By default, all output from the PlayStation TV is soft because of the following factors:
- All software has a bilinear filter applied
- All software is scaled to the PSTV's selected output resolution
- Vita software is internally scaled to 960x544p regardless of its original rendering resolution. This applies to Vita handhelds as well
- PS1 Classics are unevenly, horizontally scaled to 4:3.
To counteract this for the sharpest possible picture, we highly recommend installing custom firmware on your PSTV and installing the Sharpscale plugin to counteract all the above effects applied to the PSTV.
Sharpscale plugin
See an overview of sharpscale here. The following suggestions only work when sharpscale is enabled with the following options:
[picture of sharpscale plugin with the following settings enabled]
| Option Name | Option Choice |
|---|---|
| Scaling Mode | Integer |
| PS1 Aspect Ratio | Pixel |
| Scaling Algorithm | Point |
| Unlock Framebuffer Size | Off |
Vita Games
When Playing a Vita Game, the PSTV outputs a 960x544p picture inside of a 1280x720p canvas. Use the following settings to get the sharpest integer scaled picture for Vita Games. These settings cut off 4 vertical pixels from Vita games.
| Scaling/Crop Setup | |
| Top Trim | -90 |
| Bottom Trim | -90 |
[Picture Here: Steamworld Dig 2 with sharpscale disabled vs enabled and optimized]
PSP Games
The PSTV also outputs a 960x544p picture inside of a 1280x720p canvas. Use the following settings to get the sharpest integer scaled picture for PSP games. These settings cut off 2 vertical pixels from PSP games.
| HDMI Receiver Setup | |
|---|---|
| Input Pixels | 2 |
| Scaling/Crop Setup | |
| Top Trim | -45 |
| Bottom Trim | -45 |
| Vert. Pre-Scale | 1/2 |
[Picture Here: Final Fantasy IV with sharpscale disabled vs enabled and optimized]
PSone Classics on Vita
Sharpscale will allow you to get the sharpest picture for PS1 games, but the behavior is not optimal. With the Integer Scaling Mode setting enabled in Sharpscale, some resolutions will use the full vertical space, and others will only scale to 480 vertical pixels inside 720p. it is recommended you look at the resolutions supported by your game before you use sharpscale with the RT4K and see if it is worth avoiding the headache. If you set PS1 Aspect Ratio to 4:3 in the PSTV's settings, the PSTV will force all games to fit, but they will not evenly scale horizontally, resulting in shimmering pixels.
[Picture Here: PS1 console optimized vs pstv optimized]
Sony PlayStation 4
TurboGrafx-16/PCEngine
Microsoft Xbox
Preferred output: YPbPr.
Up to 720p available with custom firmware
Microsoft Xbox 360
The cable you should use for your Xbox 360 may vary by model.
- For Xbox 360 models made in 2007 or later, HDMI output is available and should be your first choice, since HDMI cables are readily available.
- The earliest Xbox 360 models only offer A/V video output. Unlike the PS3 and WiiU however, the 360's component video is quite sharp, so it's a good alternative to HDMI if that's what you need / prefer. A/V output was standard alongside HDMI for most of the 360's life, except for the 360 E revision.
Microsoft Xbox One
Troubleshooting
Profile Repository
Generic Profiles
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Downscaling
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Console Specific
3DO Interactive Multiplayer
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Atari Jaguar
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Microsoft Xbox
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Microsoft Xbox 360
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Neo Geo AES
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Nintendo Entertainment System (NES)
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Super Nintendo / Super Famicom
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Nintendo 64
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Nintendo Gamecube
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Nintendo Wii
| Profile Name | Download 1 | Profile Description |
|---|---|---|
| Generic | Download 2 | Recommended for use with an unhacked Wii, optimized for 240p, 480i, and 480p. |
| VC 256 | Recommended for use with the NES and Super NES Virtual Console games that output 256 wide pixels on a hacked Wii. Make sure to switch "Video Width" to Framebuffer in USBLoader GX. | |
| VC ~256 | Recommended for use with games that should be 256 pixels wide but are scaled to 320 pixels a hacked Wii. Make sure to switch "Video Width" to Framebuffer in USBLoader GX. DO NOT USE with games that actually output 256 pixels wide. | |
| VC 320 | Recommended for use with Virtual Console games that output 320 pixels wide on a hacked Wii. Make sure to switch "Video Width" to Framebuffer in USBLoader GX. |
Nintendo Wii U
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Nintendo Switch
| Profile Name | Profile Description | |
|---|---|---|
| N64 720 | Download 1 | Set the Switch to 720p to use this profile. NSO N64 games render at 720p. This profile is for use with scanlines to approximate the look on a CRT, not for additional sharpness. If you want a sharper picture, use the default profile. |
| NSO 256 | Download 2 | To be used with the NES, Super NES, and Sega Genesis Nintendo Switch Online emulators when the game has an 8:7 aspect ratio. |
| NSO 320 | Download 3 | To be used with the Sega Genesis Nintendo Switch Online emulator when the game has a 10:7 aspect ratio |
| GBA | This profile is for use with any GBA game on Switch, including the NSO GBA app as well as ports of GBA games that are scaled 6x to 1080p. This allows for a 13x scale to 2160p, where a default profile would only scale games 12x. | |
| GBC | This profile is for use with any GBC game on Switch, including the NSO GBC app as well as ports of GBC games that are scaled 7x to 1080p. This allows for a 15x scale to 2160p, where a default profile would only scale games 14x. |
Phillips CDi
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Pioneer LaserActive
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Sega Master System
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Sega Genesis / Megadrive
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Sega Saturn
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Sega Dreamcast
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Sony PlayStation 1
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Sony PlayStation 2
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Sony PlayStation 3
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Sony PSP
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Sony PlayStation TV/Vita TV
The Playstation TV profiles require a hacked PSTV and the Sharpscale plugin to take advantage of the potential sharpness the PSTV can give. If your PSTV is not hacked, please use the default profile.
For the following profiles, please set the following options in Sharpscale:
| Option Name | Option Choice |
|---|---|
| Scaling Mode | Integer |
| PS1 Aspect Ratio | Pixel |
| Scaling Algorithm | Point |
| Unlock Frame Buffer Size | Off |
| Profile Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| PSVita | Download 1 | The PlayStation TV outputs a 544p window onto a 720p canvas.
Upscaled 4x to fit 2160p. Cuts off 4 pixels vertically |
| PSP | Download 2 | Sets Decimation Factor to 2 and Prescale to 1/2
The Playstation TV outputs a line-doubled 272p window into a 720p canvas. Upscaled 8x to 2160p. Cuts off 4 pixels vertically. |
| PS1 Generic | The Playstation TV will output the PS1 game to an integer scale of its signal that will fit inside 1280x720p.
Use this profile for PS1 games that switch between many resolutions often. 480i will scale 1x. 512x224p and 640x224p will scale 2x. 384x224, 320x224, and 256x224 will scale 3x. |
The following profiles require a slight change in Sharpscale settings. These profiles are best used with games that stick to one resolution for the majority of their gameplay. Do not use these with Chrono Cross or Silent Hill, their menus will cut off vertically
| Option Name | Option Choice |
|---|---|
| Scaling Mode | Real |
| PS1 Aspect Ratio | Pixel |
| Scaling Algorithm | Point |
| Unlock Frame Buffer Size | Off |
| Profile Name | Profile Descriptions | |
|---|---|---|
| PS1 256 | Download 3 | Use for PS1 games that are primarily 256x224. |
| PS1 320 | Download 3 | Use for PS1 games that are primarily 320x224. |
| PS1 384 | Download 4 | Use for PS1 games that are primarily 384x224. |
| PS1 512 | Download 4 | Use for PS1 games that are primarily 512x224 |
| PS1 640 | Download 5 | Use for PS1 games that are primarily 640x224 |
TurboGrafx-16 / PC Engine
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | Description |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | Description |
Classic Mini Consoles
| 256 | Download 1 | Use with mini consoles that output a 3x integer scale of 8:7 aspect ratio games.
Primarily used by NES and Super NES Classic Mini consoles. Note: The Famicom Classic Mini needs Digital Video Color space changed to "Limited" |
| 320 | Download 2 | Use with mini consoles that output a 3x integer scale of 10:7 aspect ratio games.
Primarily used by Sega Genesis Classic Mini. |
Analogue Pocket
| GBA | Download 1 | Set Scale size to 6x in Pocket GBA settings. Outputs 13x scaled GBA games where the default profile would normally scale to 12x. Do not use with Pocket scanline effects. |
| GBC | Download 2 | Set Scale Size to 7x in Pocket GBC settings. Outputs 15x scaled GBC games where the default profile would normally scale to 14x. Do not use with Pocket scanline effects. |
Computer Specific
FM Towns
FM Towns computers once hitting white desktop variants output different video displays with some models performing internal upscaling conversions from 24khz to 31khz as well as some models performing 15khz to 31khz with adjustments in the TBIOS configuration file. EA and Pentium type desktops only output 31khz video modes.
The below profiles are meant for all towers, UX, UG, UR, HG and HR models which are all models that do not perform internal conversion.
FM Towns will require a custom profile for any displays at 24khz
| 24Khz | Download 1 | 24Khz Display Mode |
Sharp X68000
Sharp X68000 is unique with its outputs primarily being 15khz and 31khz. A few games have hidden selectable 24khz display modes.
| Profile Name 1 | Download 1 | 24Khz Mode in XXXX Game. |
| Profile Name 2 | Download 2 | 24Khz mode |
PC-8801
PC-8801 computers will output either 15khz or 24khz depending on the dipswitch settings in the back. If dipswitch settings are incorrect, games will refuse to boot and crash the computer.
The 15khz VGA detection in the RT4K works very well for PC8801 and most video modes won't require a profile.
A 24khz signal will require a profile to display properly.
| 24Khz Mode in BASIC | Download 1 | 24Khz Mode in BASIC. |
Advanced Features
Deinterlacer / Film Mode Setup
Motion Adaptive Settings
Motion Adaptive settings apply only to the Motion Adaptive Deinterlacing mode, allowing you to adjust it to your liking.
- Sensitivity - Adjusts the sensitivity of Motion Adaptive, between Min, Medium, High and Max. The higher this is set, the more weaving will be present for moving parts of the screen, at the benefit of a stabler look for static parts of the screen. Many games will look just fine on the Min. setting, however several games may require Medium or higher. For example, Burnout 3: Takedown on PlayStation 2 has a subtle flickering and animated noise that throws off the Motion Adaptive Deinterlacer for still parts of the screen.
Notes
Deinterlacer -> -> Motion Adaptive Settings -> Sensitivity
(medium and high options might be might be reversed) Controls combing effect at costs of sharpness. Low = less combing.
Deinterlacer -> -> Motion Adaptive Settings -> Interpolator:
Basically controls how the "bob" portion of the MA is calculated. The bob is either taken from the line above, line below or the average of the upper and lower lines BFI. It's a matter of preference. I think either Top or Bottom interpolator looks a little sharper. Average is softer In the end it doesn't matter too much because Bob is only used during motion when it is hard to see detail anwyays
Deinterlacer -> Motion Adaptive Settings -> Detector:
This is a little complicated to explain... but let me try basically symmetric adds one frame of lag but the motion detection may be better. Because it is looking "one field into the future" idk if its really better tho in real life
HDMI -> BFI Control
-Strobe: How much the frame is divided down (i.e. 1 = divide by 2, 2 = divide by 3, 3 = divide by 4) from input to output -Blur: How many frames are ON vs OFF. So let's say we are converting 60 Hz -> 240 Hz. Blur = 1, ON, OFF, OFF, OFF. Blur = 2 is ON, ON, OFF, OFF -LCD Saver - inverts the pattern of the BFI to avoid renetion. But every few minutes u will see a flicker
Custom Mode Lines
#RT4K Custom Mode Line Format #H active, H front porch, H sync, H total blank, polarity (1 = pos, 0 = neg) #V active, V front porch, V sync, V total blank, polarity (1 = pos, 0 = neg) #Nominal frame rate (floating point) #Text name
Launch Information
https://www.retrotink.com/post/introducing-the-retrotink-4k
User Guides
Custom CRT Shadow Masks
The RT4K allows for the use of custom CRT shadow mask overlays.This is primarily intended to give an effect similar to CRT slot masks, as opposed to the pictures scanlines.
- Custom CRT masks must be saved as 32-bit BMP files.
- The maximum dimensions of a CRT mask is 16 x 16 pixels. They can be smaller, which will result in denser tiling of the mask across the screen.
- A color value of 128 will be neutral,while 0 will completely black out the corresponding pixel. 255 will double the input value (although this will be clamped).
- CRT masks will NOT adhere to the pixel grid like the RT4K's scanlines will. You can make this happen yourself by having your overlay match the dimensions of a single pixel, but this will vary depending on many factors, and so should be paired with a specific Profile.
Downscaling (pre-scale) Basics
Downscaling is the act of taking a picture that's one size and reducing it to a lower resolution. This process is essential for applying thicker scanlines to a high resolution image.
- IMPORTANT: Downscaling is different from the process of having the RetroTINK-4K output a resolution lower than the source. That can be accomplished with a custom Output Resolution modeline.
For HDMI sources, this will be handled in Advanced Settings > HDMI Receiver Setup. Input Pixels determines how much the signal is "divided" by (with the number in brackets marking the effective vertical resolution). Output pixels also does something, I've heard. Initial Phase adjusts which pixels "survive" the division.
RetroTINK-4K GUI Map
Basic Setup
Input Selection
More information concerning inputs can be found in the Inputs section.
| Front | |
|---|---|
| Composite | Selects the front composite input. |
| S-Video | Selects the front s-video input. |
| RCA | |
|---|---|
| YPbPr | Selects the rear RCA YPbPr input. |
| RGsB | Selects the rear RCA RGsB input. |
| CVBS on Green | Selects the rear RCA CVBS input. |
| SCART | |
|---|---|
| RGBS (75 ohm) | Selects the SCART input and sets it to RGBS |
| RGsB | Selects the SCART input and sets it to RGsB |
| YPbPr | Selects the SCART input and sets it to YPbPr |
| CVBS on Pin 20 | information |
| CBVS on Green | information |
| Y/C on Pin 20/Red | information |
| HD-15 | |
|---|---|
| RGBHV | information |
| RGBS | information |
| RGsB | information |
| YPbPr | information |
| CBVS on Hsync | information |
| CBVS on Green | information |
| Y/C on Green/Red | information |
| Digital Video | |
|---|---|
| thing a | information |
| thing b | information |
Digital Video Output
More information concerning outputs can be found in the Outputs section.
| Transmitter | |
|---|---|
| HDR | Enables "HDR10 [8-bit]" |
| Colorimetry | Lets you choose between "Auto", "Rec. 709", "Rec. 2020", "Adobe RGB" and "Display-P3".
With HDR enabled, Rec. 2100 is also available via the "Auto" setting. |
| Sync Lock | Lets you choose between "Triple Buffer", "Gen 50.0 Hz (x1)" and "Frame 50.0 Hz (x1)". |
| VRR | Lets you choose between "Off" and "FreeSync". |
| Deep Color | Lets you choose between "Off" and "On". Exceeds the HDMI 2.1 bandwidth spec if used with 4K60 output. |
| BFI Control | |
|---|---|
| Strobe | information |
| Blur | information |
| LCD Saver | information |
| Output Resolution | |
|---|---|
| 4K60 | Sets the output to 3840x2160p at 60 frames per second |
| 4K50 | Sets the output to 3840x2160p at 50 frames per second |
| 1080p60 | Sets the output to 1920x1080p at 60 frames per second |
| 1080p50 | Sets the output to 1920x1080p at 50 frames per second |
| 1080p100 | Sets the output to 1920x1080p at 100 frames per second |
| 1440p100 | Sets the output to 2560x1440p at 100 frames per second |
| 1080p120 | Sets the output to 1920x1080p at 120 frames per second |
| 1440p120 | Sets the output to 2560x1440p at 120 frames per second |
| 480p60 | Sets the output to 640x480p at 60 frames per second |
Profiles
| Load Profile | |
|---|---|
| Load From File | Loads a chosen profile from the "profile" folder on the SD card. |
| Load Default | Loads the Default Profile. |
| Save Profile | |
|---|---|
| Save Current | Saves the current profile by overwriting the original file on the SD card. |
| Save As New | Saves the current profile as "New Profile #". |
| Assign Profile | |
|---|---|
| Button 1 | Sets a specified profile on the SD card to Button 1 on the remote. |
| Button 2 | Sets a specified profile on the SD card to Button 2 on the remote. |
| Button 3 | Sets a specified profile on the SD card to Button 3 on the remote. |
| Button 4 | Sets a specified profile on the SD card to Button 4 on the remote. |
| Button 5 | Sets a specified profile on the SD card to Button 5 on the remote. |
| Button 6 | Sets a specified profile on the SD card to Button 6 on the remote. |
| Button 7 | Sets a specified profile on the SD card to Button 7 on the remote. |
| Button 8 | Sets a specified profile on the SD card to Button 8 on the remote. |
| Button 9 | Sets a specified profile on the SD card to Button 9 on the remote. |
| Button 10 | Sets a specified profile on the SD card to Button 10 on the remote. |
| Button 11 | Sets a specified profile on the SD card to Button 11 on the remote. |
| Button 12 | Sets a specified profile on the SD card to Button 12 on the remote. |
| Power Up | Sets a specified profile on the SD card to load when the RT4K is powered up. |
Advanced Settings
Scaling/Cropping
| Input Crop | |
|---|---|
| Top Trim | Adjusts trim on the top edge of the picture. |
| Bottom Trim | Adjusts trim on the bottom edge of the picture. |
| Left Trim | Adjusts trim on the left edge of the picture. |
| Right Trim | Adjusts trim on the right sedge of the picture. |
| Vert. Pre-Scale | Reduces the effective vertical resolution of an HDMI image. Can be set between "1/2" and "1/31". |
| RoTATE (Beta) | information |
| CP Auto Crop | |
|---|---|
| Vertical Only | Crops only the top and bottom edges of the image, sets Aspect Correction to "4:3 (PAR)" and Scaling Mode to "Proportional". |
| Full Crop to 4:3 | Crops all edges of the image, sets Aspect Correction to "4:3 (PAR)" and Scaling Mode to "Proportional". |
| Full Crop to 16:9 | Crops all edges of the image, sets Aspect Correction to "16:9 (PAR)" and Scaling Mode to "Proportional". |
| Scaler | |
|---|---|
| Aspect Correction | Lets you choose between "4:3 (PAR)", "16:9 (PAR)" and "1:1 (Sq. Pixel)" options. |
| Scaling Mode | Lets you choose between "Auto Fill", "Proportional", "Free-Form" and "Auto Fill Integer" options. |
| Vert. Factor | Adjusts the vertical height of the image. Only available when Scaling Mode is set to "Proportional" or "Free-Form". |
| Hori. Factor | Adjusts the Horizontal width of the image. Only available when Scaling Mode is set to "Free-Form". |
| Buffer | |
|---|---|
| Length | Displays the current lag in milliseconds. Can be set to "Min. Lag", "1/2 Frame" or "1 Frame". |
| Masking Color | |
|---|---|
| Red | Adds red to the cropping mask, between 0 and 31. |
| Green | Adds green to the cropping mask, between 0 and 31. |
| Blue | Adds blue to the cropping mask, between 0 and 31. |
| Show | Lets you choose between "Cropping Only" and "Always". |
Processing / Effects
| Interpolation | |
|---|---|
| Vert. Kernel | Lets you choose between "Bilinear Sharp", "Bilinear Med.", "Bilinear Std.", "Bilinear Soft", "Cubic", "Lanczos2", "Lanczos3", "Sinc", and "None". |
| Hori. Kernel | Lets you choose between "Bilinear Sharp", "Bilinear Med.", "Bilinear Std.", "Bilinear Soft", "Cubic", "Lanczos2", "Lanczos3", "Sinc", and "None". |
| Anti-Ringing | Can be set to "On" or "Off". Only visible on "Lanczos2" and "Lanczos 3". |
| Scanline | |
|---|---|
| Function | Lets you choose between "Off", "Exponential", "Gaussian", "Super Gaussian", "Linear", "Box", "LCD Mono" and "LCD RGB". Anything except for "Off" will enable the settings below. |
| Strength | Increases scanline strength from 0 to 99. |
| Modulation | Increases modulation strength from 0 to 99. |
| Red Bleed | Enables red bleed. |
| Red Convergence | Adjusts red convergence from -10 to 10. |
| Blue Convergence | Adjusts blue convergence from -10 to 10. |
| Mask | |
|---|---|
| Enable | Enables the Mask feature, as well as the Strength option. Will not appear to do anything until "Load from File" is used. |
| Strength | Adjusts the mask strength from -10 to 10. |
| Load from File | Select a Mask File from the "mask" folder on the SD card. |
| Horizontal Blur | |
|---|---|
| Function | Lets you choose between "Off" and "IIR LPF", enabling the Cut-Off Freq option below. |
| Cut-Off Freq | Adjusts the blur strength from 0.50 MHz to 9.00 MHz, in 0.25 increments. |
Color Correction
| Gamma/Linear Light/HDR | |
|---|---|
| Input Factor | Can be adjusted between 0.99 and 5.00. |
| Input Lift | Can be adjusted between -1.00 and 1.00. |
| Input Gain | Can be adjusted between 0.00 and 10.00. |
| Output Factor | Can be adjusted between 0.10 and 5.00. |
| SMPTE 2048 PQ | information |
| Color Space Conversion | |
|---|---|
| Custom Matrix | Enables the Input RGB to XYZ options below. |
| Load from SD | Lets you load a CSC file from the "csc" folder on the SD card. |
| Input RGB to XYZ | |
|---|---|
| Xo[Rin] | Can be adjusted between -1.75000 to +1.75000. |
| Xo[Gin] | Can be adjusted between -1.75000 to +1.75000. |
| Xo[Bin] | Can be adjusted between -1.75000 to +1.75000. |
| Yo[Rin] | Can be adjusted between -1.75000 to +1.75000. |
| Yo[Gin] | Can be adjusted between -1.75000 to +1.75000. |
| Yo[Bin] | Can be adjusted between -1.75000 to +1.75000. |
| Zo[Rin] | Can be adjusted between -1.75000 to +1.75000. |
| Zo[Gin] | Can be adjusted between -1.75000 to +1.75000. |
| Zo[Bin] | Can be adjusted between -1.75000 to +1.75000. |
| Misc. | |
|---|---|
| Bit Crush | Lowers the color depth of the picture. Can be adjusted between "Off" and "7 bits Removed". |
| Transfer Function | Can be set to "sRGB 0.055", "Rec.601/709 0.099", "SMPTE 240M 0.1115" or "Gamma". |
Black Frame Insertion
| BFI Insertion | |
|---|---|
| Strobe | information |
| Blur | information |
| LCD Saver | information |
| BFI Color | |
|---|---|
| Blending Mode | Lets you choose between "Solid" and "Alpha". |
| Red | Adjusts Red, Green and Blue from 0 to 31. |
| Green | Adjusts Red, Green and Blue from 0 to 31. |
| Blue | Adjusts Red, Green and Blue from 0 to 31. |
Deinterlacer / Film
| Mode | |
|---|---|
| Algorithm: | Lets you choose between "Motion Adaptive", "Weave", "Bob", "Linear", "Blend", "CRT Simulation" and "LCD Blending". |
| Field Inversion: | Reverses the fields of 480i signals. Can be set to "Off" or "On". |
| Motion Adaptive Settings | |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Adjusts the sensitivity of the Motion Adaptive Deinterlacer. Can be set to "Low", "Medium", "High" and "Max". Higher settings result in a more solid image but with more weaving artifacts. |
| Noise Threshold | Adjusts the noise threshold, at the cost of weaving. Can be adjusted between 0 and 63. |
| Interpolator | Choose which field to prioritize. Can be set to "Average", "Bottom Field" and "Upper Field" |
| Detector | Can be set to "Zero-lag" or "Symmetric". |
| Bob Settings | |
|---|---|
| Offset | Adjusts how far each field is shifted when using the "Bob" Algorithm. Can be set between -3 and +3. |
| Film Mode | |
|---|---|
| Inverse Telecine | Enables a detector for "3:2" telecine (24fps content) and "2:2" telecline (30fps content). |
| Dejudder 24 Hz | Can be set to "Off" or "On". |
| Cadence Detection | |
|---|---|
| Motion Digital | Can be set from 0 to 500. |
| Motion CP | Can be set from 0 to 500. |
| Motion SDP | Can be set from 0 to 500. |
| Threshold | Can be set from 0 to 500. |
Acquisition
Digital In Receiver
| Input Decimation | |
|---|---|
| Input Pixels | information |
| Output Pixels | information |
| Initial Phase | information |
| Colorspace | |
|---|---|
| 4:2:2 Upsampler | information |
| Input Range | information |
| Input RGB range | information |
RGB / Component ADC
| Sampling | |
|---|---|
| Samples per Line | Manually set the sampling. |
| Decimation Factor | Can be set to between 2 and 16. |
| Decimation Phase | Value range matches the Decimation Factor. |
| Sub-Phase | Adjusts the Sub-Phase in 11.25 increments. Can be set as high as "348.75 deg" |
| Anti-Alias LPF | Can be set to "Auto (16MHz)", "9MHz (Strong)", "16 MHz (Med)", "35 MHz (Light)", "95 MHz (Min.)" and "Off". |
| Sync | |
|---|---|
| SoG Threshold | Adjusts the Sync on Green Threshold in 11.29 increments. Can be set between "0.00 mV" and "327.42 mV". |
| Pre-coast | Can be set between 1 and 31. |
| Post-coast | Can be set between 1 and 31. |
| Slow-lock | Gives more time to lock onto Sync on Green. Can be set to "Off" or "On". |
| Gain | |
|---|---|
| Pre-ADC | Adjusts the picture gain. Can be set between -0.7 and +0.8. |
| Red | Adds red to the picture, in increments of 0.008. Can be adjusted between 1.000 and 1.996. |
| Green | Adds green to the picture, in increments of 0.008. Can be adjusted between 1.000 and 1.996. |
| Blue | Adds blue to the picture, in increments of 0.008. Can be adjusted between 1.000 and 1.996. |
| Offset | |
|---|---|
| Red | Can be set between -100 and +100. |
| Green | Can be set between -100 and +100. |
| Blue | Can be set between -100 and +100. |
| Auto Calibrate | |
|---|---|
| Phase | Analyzes the picture to determine the Sub-Phase setting. Works best on detailed images with high contrast details. |
| Gain | Analyzes the picture to determine the Red, Green and Blue Phase settings. Works best on calibration screens like in the 240p Test Suite. |
Sample Rate Detection
| Control | |
|---|---|
| Auto Dec. Factor | Can be set to "Off" or "On". Enables all other options in the Sample Rate Detection Menu |
| Auto Dec. Phase | Can be set to "Off" or "Auto". |
| ADC Sample Rate | Manually set the sampling. |
| Progressive Detection | |
|---|---|
| Enable Sample Rate A | information |
| Enable Sample Rate B | information |
| Enable Sample Rate C | information |
| Enable Sample Rate D | information |
| Enable Sample Rate E | information |
| Enable Sample Rate F | information |
| Interlaced Detection | |
|---|---|
| Enable Sample Rate A | information |
| Enable Sample Rate B | information |
| Enable Sample Rate C | information |
| Enable Sample Rate D | information |
| Enable Sample Rate E | information |
| Enable Sample Rate F | information |
SDP Decoder
| Gain / Balance | |
|---|---|
| Brightness | information |
| Contrast | information |
| Chroma | information |
| Phase | information |
| Blue Only | information |
| Setup | information |
| Processing | |
|---|---|
| Y/C Filter | information |
| Comb Bandwidth | information |
| Chroma Badwidth | information |
| Sharpness | information |
| CTIE | information |
| Sync | |
|---|---|
| H-Lock Speed | information |
| Standard | information |
Audio Input
| Sampling | |
|---|---|
| Sample Rate | Can be set to "48 kHz" or '96 kHz". |
| Pre-amp Gain | Can be set between "-24.0 dB" and "+28.0 dB" in 0.5 increments. |
| Source | |
|---|---|
| Input Override | Manually changed the audio input to another source. Can be set to "Off", "RCA", "HD-15", "SCART", "Front" or "S/PDIF". |
| Input Swap | Can be set to "Mono (Left)", "Mono (Right" or "L/R Swap". |
System
OSD / Firmware
| On Screen Display | |
|---|---|
| Position | Can be set to "Left", "Center" and "Right". |
| Auto-Off | Sets the time the menu will disable after inactivity. Can be set up to "100 sec" in 10 sec increments. |
| Load Banner | Loads a menu banner from the "image" folder on the SD card. |
| Enable Debug OSD | Permenantly displays one of the debug OSDs on the screen. Can be set to "Off", "Status Pg 1", "Status Pg 2", "Status Pg 3" or "Console". |
| Firmware Update | |
|---|---|
| Check SD Card | Checks the SD card for update files stored in the SD card's root directory. If multiple firmware files are present, the most recent one will be chosen. |
Status
| Status |
|---|
| Lets one display one of three System Status pages relating to the RT4K. |
Device
Status
System Status Page 1:
| Video Source | |
|---|---|
| Video Source | CP Proc. (I assume CP Proc will change based on selection) |
| Input Timing | information |
| Pixel Clock | information |
| Freq | information |
| Detected Mode | information |
| Audio Input | |
|---|---|
| Audio Input | I2S (I assume will change based on audio input) |
| Measured Freq | information |
| Measured Freq | information |
| HDMI N / CTS | information |
| FPGA Core | |
|---|---|
| Scaler Clock | information |
| PLL VCO | information |
| Pipeline | information |
| SDRAM Clock | information |
| SDRAM Load | information |
| HDMI Transmitter | |
|---|---|
| Output Timing | information |
| Active Size | information |
| Pixel Clock | information |
| HDMI Standard | information |
| PIC32MX MCU | |
|---|---|
| System Clock | information |
| Uptime | information |
| Loop Time | information |
| Last IR Code | information |
| SD Card Free | information |
System Status Page 2:
| HDMI Input Protocol Analyzer | |
|---|---|
| TMDS | information |
| Mode | information |
| Resolution | information |
| Colorspace | information |
| H. Timing | information |
| V. Timing (F0) | information |
| V. Timing (F1) | information |
| Audio | information |
| AVI Infoframe | information |
| Aud. Infoframe | information |
| VS Infoframe | information |
| ACP Infoframe | information |
System Status Page 3:
| HDMI TX Information | |
|---|---|
| TX Mode | information |
| Hot Plug | information |
| Scrambling | information |
| Clock Factor | information |
| Ch 0 Error | information |
| Ch 1 Error | information |
| Ch 2 Error | information |
| Sink EDID Dump | information |
Diagnostic Console
to do
| Diagnostic Console |
|---|
| Displays a diagnostic console screen regarding Digital In TX channels. |
About
| About | |
|---|---|
| About | Displays the name of the device, the firmware version, and the Device ID. |
| Resorces | Displays the URLs for the RetroTINK website, Discord channel, and the RetroTINK-4K wiki page. |
| Thanks! | Displays a thank you message from Mike Chi to the user. |